A roof mounted bicycle carrier can have a significant impact on an electric car's range, a new study has found.
AVILOO, a specialist in electric vehicle (EV) battery diagnostics, compared the driving efficiency of a VW ID4 when equipped with a roof mounted bicycle carrier, a rear-mounted bicycle carrier and with no bicycle carrier.
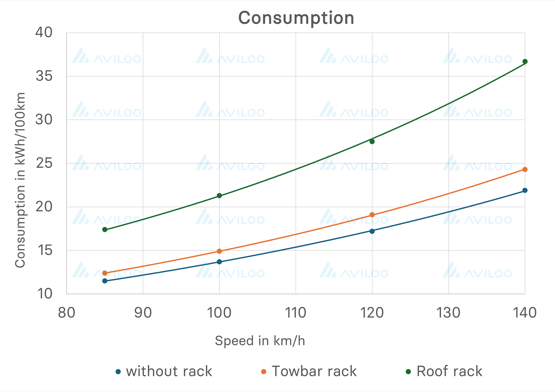
At a speed of 120km/h (75mph), the ID4 returned around 3.5mi/kWh. That dropped to just 2.3mi/kWh when the roof mounted carrier was fitted, reducing the car's overall range by 92 miles.
The study found that someone accustomed to driving at 130km/h (81mph) would need to reduce their speed by a full 33km/h to 97km/h (60mph) to achieve the same consumption level as when driving without any load
Switching to rear mounted carrier saw a much less drastic reduction in efficiency to 3.2mi/kWh.
“We want to bring clarity with our study,” explains Nikolaus Mayerhofer, CTO of AVILOO and test driver for all test rounds. “There are many half-truths about extra consumption due to loading. Our measurements clearly show that rear-mounted racks have minimal impact on range and driving behaviour. Roof loads, however, result in noticeable losses. The main physical reason for the clear differences is air resistance - it doesn’t increase linearly but quadratically. At double the speed, air resistance increases energy use fourfold.”
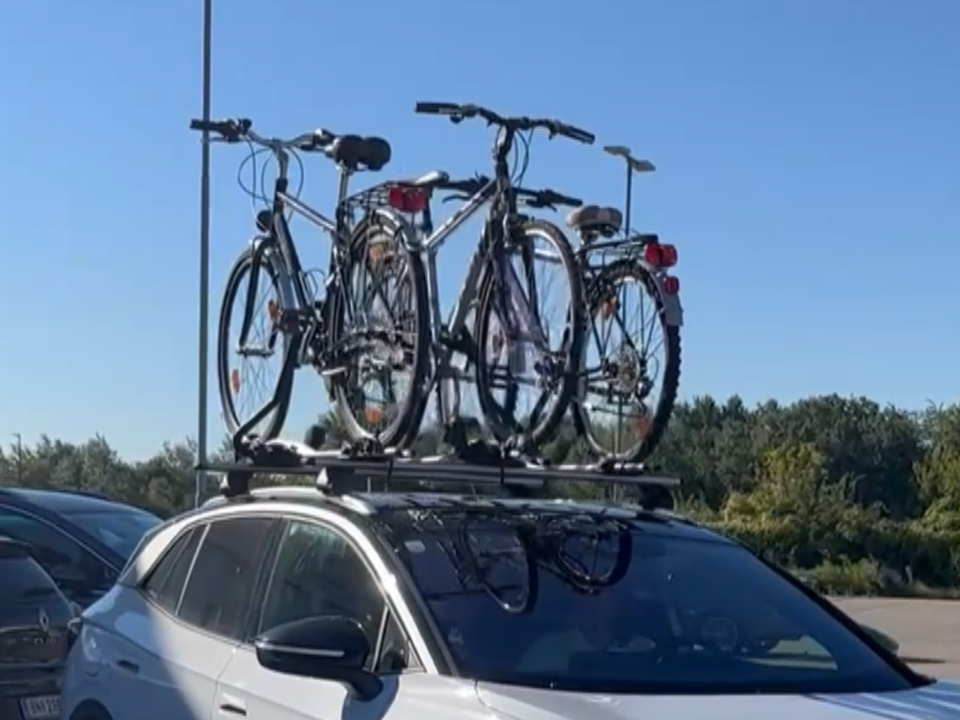
The test was carried out in controlled conditions in Vienna. The load consisted of three 28-inch trekking bikes and each configuration was tested at night (to avoid traffic influence) over a fixed 60km round-trip route.
The following fixed test parameters, self-influenced variables, and external conditions were consistently maintained and considered: constant speed (via cruise control), tyre pressure, summer tyres, no air conditioning or heating, closed windows, dry road surface, and wind speed under 15km/h. AVILOO said these unchanging baseline conditions ensured meaningful and reproducible measurements.



















Login to comment
Comments
No comments have been made yet.